The Major Battles of WW2 Map Worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of the key battles of World War II, their geographical distribution, and their strategic significance. This worksheet is an invaluable resource for students, historians, and anyone interested in understanding the course and impact of this global conflict.
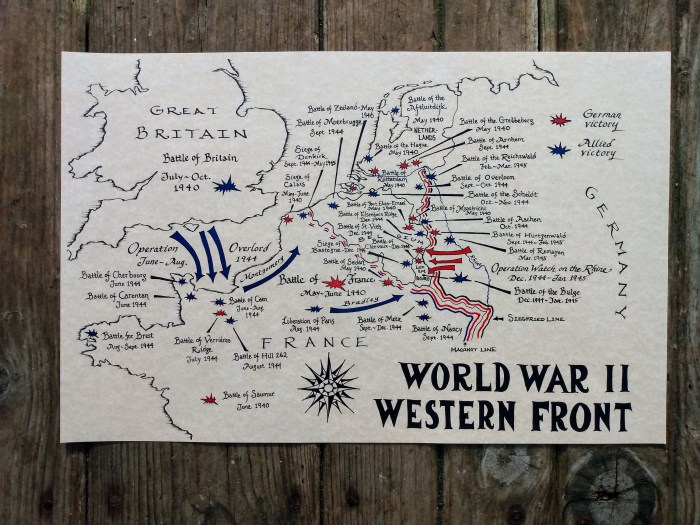
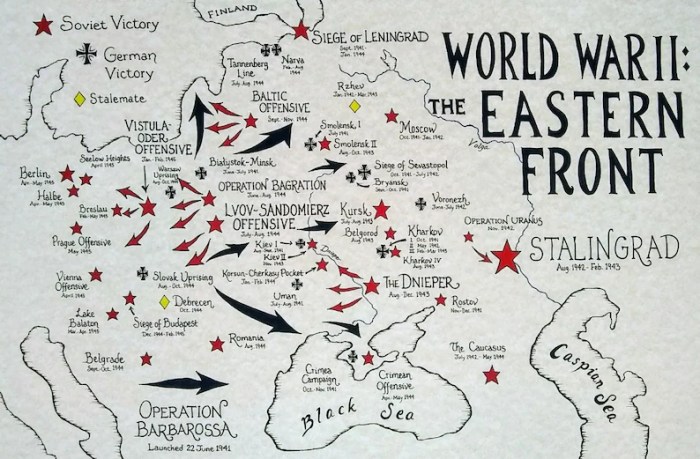
The worksheet includes a detailed map of the major battles, highlighting their locations and proximity to key strategic areas. It also provides a timeline of the key battles and their strategic importance, as well as information on the key players and strategies involved in each battle.
Historical Overview of Major Battles in WW2
Major battles in World War II had a profound impact on the course of the conflict, shaping its outcome and redrawing the geopolitical map of the world. These battles were pivotal in determining the fate of nations, testing the limits of human endurance, and showcasing the destructive power of modern warfare.
The timeline of key battles is as follows:
- September 1939: Invasion of Poland– Marked the beginning of WW2, as Germany invaded Poland.
- May-June 1940: Battle of France– Germany’s swift victory over France, leading to its occupation.
- June 1941: Operation Barbarossa– Germany’s invasion of the Soviet Union, the largest land invasion in history.
- December 7, 1941: Attack on Pearl Harbor– Japan’s surprise attack on the US naval base, bringing the US into the war.
- Midway (June 1942) and Guadalcanal (August 1942-February 1943)– Key naval battles in the Pacific, turning the tide against Japan.
- Stalingrad (August 1942-February 1943)– A brutal urban battle that marked a turning point on the Eastern Front.
- D-Day (June 1944)– The Allied invasion of Normandy, opening a second front against Germany.
- Battle of the Bulge (December 1944-January 1945)– Germany’s last major offensive, ultimately unsuccessful.
- August 1945: Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki– Ended the war with Japan’s surrender.
Geographical Distribution of Major Battles
The map of major battles highlights their geographical distribution, revealing patterns and strategic considerations.
Key battles occurred in:
- Europe: Poland, France, Germany, Soviet Union, Italy, and the Balkans.
- Asia: China, Burma, India, and the Pacific islands.
- North Africa: Egypt, Libya, and Tunisia.
Proximity to strategic areas, such as industrial centers, resource-rich regions, and major ports, played a crucial role in determining the outcomes of these battles.
Key Players and Strategies in Major Battles
Key players in major battles included:
- Germany: Led by Adolf Hitler, Germany employed the “Blitzkrieg” strategy, relying on rapid, concentrated attacks.
- Soviet Union: Led by Joseph Stalin, the Soviet Union relied on massive manpower and industrial production to wear down its enemies.
- United States: Led by Franklin D. Roosevelt, the US provided crucial military and economic support to its allies.
- United Kingdom: Led by Winston Churchill, the UK stood alone against Germany in the early years of the war.
- Japan: Led by Emperor Hirohito, Japan sought to expand its empire in Asia and the Pacific.
Successful strategies included:
- Germany’s “Blitzkrieg”: Achieved quick victories in Poland and France.
- Soviet Union’s “Human Wave” tactics: Overwhelmed German forces in Stalingrad.
- US’s “Island Hopping” campaign: Gradually isolated Japan in the Pacific.
Unsuccessful strategies included:
- Germany’s invasion of the Soviet Union: Failed to account for the vastness and resilience of the Soviet Union.
- Japan’s attack on Pearl Harbor: Brought the US into the war and ultimately led to Japan’s defeat.
- Germany’s Battle of the Bulge: A desperate attempt to reverse the tide of the war that failed.
Impact of Technology and Logistics on Major Battles
Technology played a pivotal role in major battles:
- Radar: Enabled early detection of enemy aircraft and ships.
- Aircraft: Provided air superiority, bombing capabilities, and reconnaissance.
- Tanks: Revolutionized land warfare, providing mobility, firepower, and protection.
Logistics, including supply chains and transportation, were crucial:
- Germany’s supply lines: Overextended in the Soviet Union, leading to shortages and setbacks.
- US’s lend-lease program: Provided vital supplies to its allies.
- Japan’s lack of resources: Contributed to its eventual defeat.
Political and Diplomatic Implications of Major Battles
Major battles had significant political and diplomatic consequences:
- Formation of alliances: Battles brought nations together, such as the Allied Powers and the Axis Powers.
- Post-war order: Battles shaped the post-war world, leading to the creation of the United Nations and the division of Europe.
- Diplomatic negotiations: Battles influenced diplomatic negotiations, such as the Tehran Conference and the Yalta Conference.
Legacy and Remembrance of Major Battles: Major Battles Of Ww2 Map Worksheet
Major battles have a lasting legacy:
- Historical significance: Battles are remembered as turning points in history and are studied by historians.
- Collective memory: Battles shape collective memory and national identities.
- Commemoration: Battles are commemorated through memorials, museums, and ceremonies.
Common Queries
What is the purpose of the Major Battles of WW2 Map Worksheet?
The purpose of the Major Battles of WW2 Map Worksheet is to provide a comprehensive overview of the key battles of World War II, their geographical distribution, and their strategic significance.
What information does the worksheet include?
The worksheet includes a detailed map of the major battles, highlighting their locations and proximity to key strategic areas. It also provides a timeline of the key battles and their strategic importance, as well as information on the key players and strategies involved in each battle.
Who is the worksheet intended for?
The worksheet is intended for students, historians, and anyone interested in understanding the course and impact of World War II.