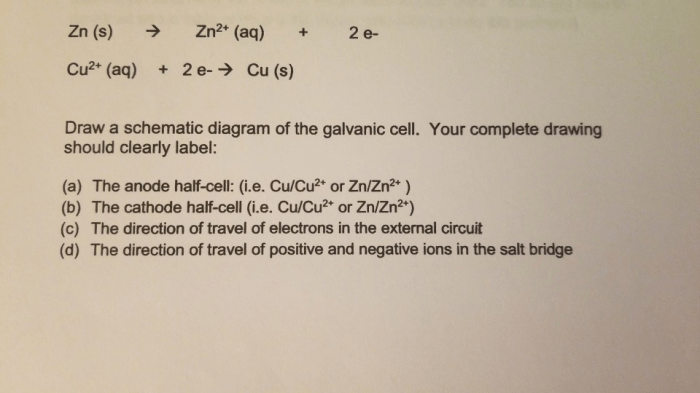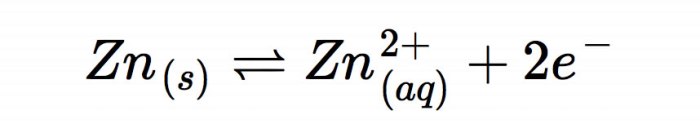Which half reaction correctly represents oxidation – Which half-reaction correctly represents oxidation? This question lies at the heart of understanding redox reactions, where the transfer of electrons drives chemical transformations. In this comprehensive analysis, we delve into the intricate relationship between electron loss and oxidation, exploring how to identify oxidizing agents and interpret oxidation state changes.
Through detailed examples and authoritative insights, we unravel the complexities of oxidation half-reactions, providing a thorough understanding for students and researchers alike.
Half-Reaction Identification

Half-reactions represent the individual processes of oxidation and reduction that occur in redox reactions. Oxidation is the loss of electrons, while reduction is the gain of electrons.
In half-reactions, electron transfer is explicitly shown. The species that undergoes oxidation is known as the reductant, while the species that undergoes reduction is known as the oxidant.
Electron Loss and Oxidation, Which half reaction correctly represents oxidation
Oxidation is the loss of electrons from a species. When a species loses electrons, its oxidation state increases. Oxidation state is a measure of the relative electron charge of an atom in a molecule or ion.
For example, in the reaction Fe → Fe 3++ 3e –, iron loses three electrons and its oxidation state increases from 0 to +3.
Oxidation State Changes
Oxidation state changes can be determined by comparing the oxidation state of the species before and after the reaction. A positive change in oxidation state indicates oxidation, while a negative change indicates reduction.
In the reaction Cu +→ Cu 2++ e –, copper loses one electron and its oxidation state increases from +1 to +2.
Identifying Oxidizing Agents
Oxidizing agents are species that accept electrons and cause other species to undergo oxidation. They typically have a high affinity for electrons.
Common oxidizing agents include oxygen (O 2), chlorine (Cl 2), and potassium permanganate (KMnO 4). These oxidizing agents can accept electrons from other species, causing them to undergo oxidation.
Question Bank: Which Half Reaction Correctly Represents Oxidation
What is the difference between oxidation and reduction?
Oxidation is the loss of electrons, while reduction is the gain of electrons.
How do I identify oxidizing agents?
Oxidizing agents are substances that accept electrons and undergo reduction.
What is the significance of oxidation state changes in half-reactions?
Oxidation state changes indicate the transfer of electrons and help balance redox reactions.