Welcome to the Skills Module 3.0 Airway Management Pretest, an immersive journey into the intricacies of airway management. This comprehensive guide empowers you with a deep understanding of the techniques, anatomy, assessment, equipment, procedures, algorithms, and simulations involved in this critical aspect of patient care.
As you delve into the following sections, you will gain invaluable knowledge and insights that will equip you to confidently navigate airway management challenges and ensure optimal patient outcomes. Prepare to enhance your skills and elevate your proficiency in this essential area of healthcare practice.
Airway Management Techniques
Airway management is the process of maintaining a patent airway in patients who are unable to maintain their own airway. There are a variety of airway management techniques that can be used, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Oropharyngeal Airway
An oropharyngeal airway (OPA) is a curved plastic tube that is inserted into the mouth and extends into the pharynx. OPAs are used to maintain a patent airway in patients who are unconscious or have a decreased level of consciousness.
They are relatively easy to insert and can be used in a variety of settings.
Nasopharyngeal Airway
A nasopharyngeal airway (NPA) is a soft, flexible tube that is inserted into the nose and extends into the pharynx. NPAs are used to maintain a patent airway in patients who are conscious or have a gag reflex. They are less likely to cause discomfort than OPAs, but they can be more difficult to insert.
Supraglottic Airway
A supraglottic airway (SGA) is a device that is placed in the oropharynx above the glottis. SGAs are used to maintain a patent airway in patients who are unable to tolerate an OPA or NPA. They are more difficult to insert than OPAs or NPAs, but they are less likely to cause trauma.
Endotracheal Tube
An endotracheal tube (ETT) is a tube that is inserted into the trachea through the mouth or nose. ETTs are used to maintain a patent airway in patients who are unable to breathe on their own. They are the most invasive airway management technique, but they are also the most effective.
Airway Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy of the Airway
The airway is a series of passages that allow air to flow from the nose and mouth to the lungs. The upper airway includes the nose, pharynx, and larynx. The lower airway includes the trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles.
Physiology of Respiration
Respiration is the process of exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide between the body and the environment. Respiration occurs in the lungs, where oxygen is taken up from the air and carbon dioxide is released into the air.
Factors that can Affect Airway Patency
A number of factors can affect airway patency, including:
- Trauma
- Infection
- Foreign bodies
- Tumors
- Edema
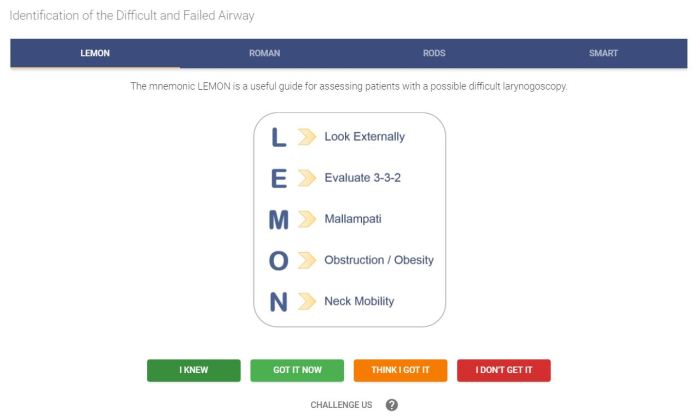
Airway Assessment
Airway assessment is the process of evaluating a patient’s airway to determine if it is patent. Airway assessment should be performed in all patients who are unconscious, have a decreased level of consciousness, or have any signs or symptoms of airway compromise.
Signs and Symptoms of Airway Compromise, Skills module 3.0 airway management pretest
The signs and symptoms of airway compromise include:
- Stridor
- Wheezing
- Cyanosis
- Dyspnea
- Apnea
Importance of Early Airway Assessment
Early airway assessment is important because it allows for early intervention to maintain a patent airway. Early intervention can prevent serious complications, such as hypoxia and cardiac arrest.
Airway Management Equipment
There are a variety of airway management equipment that can be used to maintain a patent airway. The most common types of airway management equipment include:
- Oropharyngeal airways
- Nasopharyngeal airways
- Supraglottic airways
- Endotracheal tubes
- Bag-valve-mask
- Suction
Importance of Proper Equipment Selection
The proper selection of airway management equipment is important for maintaining a patent airway. The type of equipment that is selected will depend on the patient’s condition and the provider’s experience.
Airway Management Procedures
Airway management procedures are the steps that are taken to maintain a patent airway. The steps involved in airway management procedures will vary depending on the type of airway management equipment that is being used.
Indications for Airway Management
Airway management is indicated in patients who are unable to maintain their own airway. This can occur in a variety of situations, including:
- Unconsciousness
- Decreased level of consciousness
- Airway obstruction
- Respiratory failure
Risks and Complications of Airway Management
Airway management procedures are not without risks. The risks and complications of airway management include:
- Trauma
- Infection
- Aspiration
- Hypoxia
- Cardiac arrest
Airway Management Algorithms
Airway management algorithms are a set of guidelines that can be used to guide the provider in the selection and use of airway management equipment. The most common airway management algorithms include:
- The American Heart Association (AHA) Airway Management Algorithm
- The European Resuscitation Council (ERC) Airway Management Algorithm
- The National Emergency Airway Registry (NEAR) Airway Management Algorithm
Advantages and Disadvantages of Airway Management Algorithms
Airway management algorithms have a number of advantages, including:
- They provide a standardized approach to airway management.
- They can help to reduce the risk of errors.
- They can improve patient outcomes.
Airway management algorithms also have a number of disadvantages, including:
- They can be complex and difficult to follow.
- They may not be appropriate for all patients.
- They may not be able to account for all possible scenarios.
Airway Management Simulation

Airway management simulation is the use of simulation to train providers in airway management techniques. Airway management simulation can be used to teach providers how to select and use airway management equipment, how to perform airway management procedures, and how to manage airway emergencies.
Importance of Airway Management Simulation
Airway management simulation is important because it allows providers to practice airway management techniques in a safe and controlled environment. This can help to improve provider confidence and competence, and can reduce the risk of errors in the clinical setting.
Types of Airway Management Simulators
There are a variety of airway management simulators that are available. The type of simulator that is used will depend on the provider’s needs and the level of training that is desired.
Benefits of Using Airway Management Simulators
Airway management simulation offers a number of benefits, including:
- Improved provider confidence and competence
- Reduced risk of errors in the clinical setting
- Opportunity to practice airway management techniques in a safe and controlled environment
- Ability to learn from mistakes without harming patients
General Inquiries: Skills Module 3.0 Airway Management Pretest
What is the purpose of the Skills Module 3.0 Airway Management Pretest?
The pretest serves as an assessment tool to gauge your current knowledge and understanding of airway management concepts and techniques.
What topics are covered in the Skills Module 3.0 Airway Management Pretest?
The pretest encompasses a wide range of topics, including airway management techniques, anatomy and physiology, assessment, equipment, procedures, algorithms, and simulation.
How can I prepare for the Skills Module 3.0 Airway Management Pretest?
Thoroughly review the provided study materials, engage in self-study, and consider seeking guidance from experienced airway management professionals.