Unveiling the Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answer Key, this comprehensive guide embarks on an enlightening journey into the intricate processes that sustain life. Delving into the depths of these fundamental biological mechanisms, we unravel the secrets of energy conversion and the intricate interplay between plants and animals.
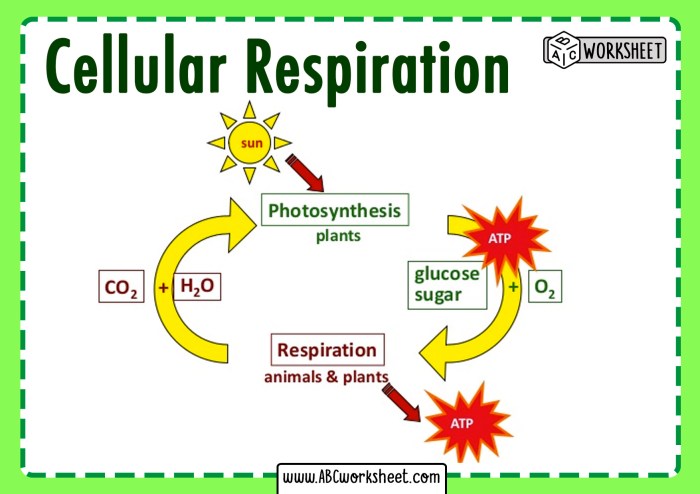
Photosynthesis, the lifeblood of plants, harnesses the power of sunlight to transform carbon dioxide and water into glucose, the fuel that drives cellular activities. Cellular respiration, on the other hand, utilizes glucose to generate energy for all living organisms, releasing carbon dioxide and water as byproducts.
Together, these processes form an intricate cycle that sustains the delicate balance of life on Earth.
Introduction
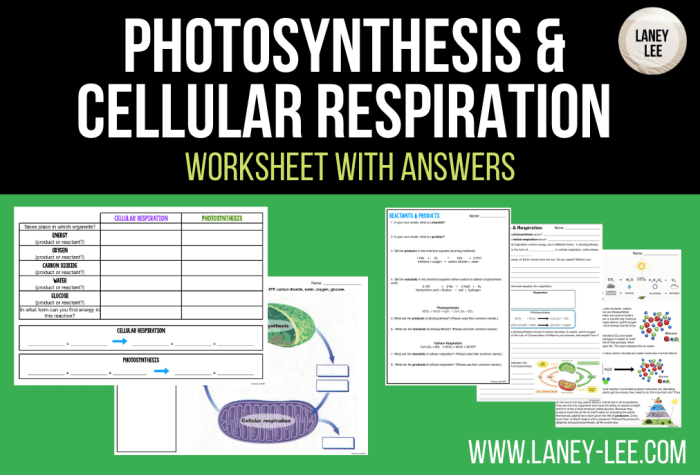
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are fundamental processes that sustain life on Earth. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants and other organisms use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. Cellular respiration, on the other hand, is the process by which organisms break down glucose to produce energy in the form of ATP.
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis occurs in two stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions. The light-dependent reactions take place in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts and use light energy to produce ATP and NADPH. The light-independent reactions, also known as the Calvin cycle, take place in the stroma of chloroplasts and use ATP and NADPH to fix carbon dioxide into glucose.
Chlorophyll is a green pigment that plays a crucial role in photosynthesis. It absorbs light energy from the sun and uses it to power the light-dependent reactions. Other pigments, such as carotenoids and phycobilins, also help to absorb light energy and protect chlorophyll from damage.

Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration occurs in three stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm and breaks down glucose into two molecules of pyruvate. The Krebs cycle takes place in the mitochondria and further breaks down pyruvate to produce carbon dioxide, ATP, and NADH.
The electron transport chain takes place in the inner membrane of mitochondria and uses NADH to produce ATP.
Oxygen is essential for cellular respiration. It is used as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain.
| Glycolysis | Krebs Cycle | Electron Transport Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Occurs in the cytoplasm | Occurs in the mitochondria | Occurs in the inner membrane of mitochondria |
| Breaks down glucose into two molecules of pyruvate | Further breaks down pyruvate to produce carbon dioxide, ATP, and NADH | Uses NADH to produce ATP |
| Does not require oxygen | Requires oxygen | Requires oxygen |
Energy Conversion
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are essential for energy conversion in living organisms. Photosynthesis converts light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose. Cellular respiration converts chemical energy in the form of glucose into ATP, which is the main energy currency of cells.
ATP and NADPH are two important molecules that play a role in energy metabolism. ATP is a nucleotide that stores energy in its phosphoanhydride bonds. NADPH is a coenzyme that carries electrons. Both ATP and NADPH are used to power cellular processes, such as muscle contraction and nerve impulse transmission.
Organisms use energy to perform a variety of functions, such as growth, reproduction, and movement. Energy is also used to maintain homeostasis, the stable internal environment of cells and organisms.
Applications: Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answer Key
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration have a wide range of practical applications. In agriculture, photosynthesis is used to increase crop yields by providing plants with optimal conditions for growth. In medicine, cellular respiration is used to develop new drugs and treatments for diseases such as cancer.
In biotechnology, photosynthesis and cellular respiration are used to produce biofuels and other renewable energy sources.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the primary function of photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is responsible for converting light energy into chemical energy, transforming carbon dioxide and water into glucose, the primary energy source for plants and the foundation of food chains.
How does cellular respiration differ from photosynthesis?
Unlike photosynthesis, which occurs in plants and some microorganisms, cellular respiration takes place in all living organisms and utilizes glucose to generate energy, releasing carbon dioxide and water as waste products.
What is the role of ATP in cellular respiration?
ATP (adenosine triphosphate) serves as the primary energy currency of cells, storing and releasing energy as needed to power various cellular processes.