Student exploration distance-time and velocity-time graphs – Student exploration of distance-time and velocity-time graphs unveils a captivating realm of graphical representations that illuminate the intricate dance of motion. These graphs empower students to decipher the dynamics of objects in motion, unraveling the secrets of their displacement and speed over time.
By embarking on this exploration, students not only gain a deeper understanding of fundamental physics concepts but also develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills that extend far beyond the classroom.
Distance-time graphs chronicle the journey of an object, mapping its displacement against the relentless march of time. Velocity-time graphs, on the other hand, capture the object’s velocity, revealing its fluctuations and providing insights into its acceleration and deceleration. Together, these graphs paint a vivid picture of an object’s motion, enabling students to visualize and analyze its trajectory.
Student Exploration of Distance-Time and Velocity-Time Graphs: Student Exploration Distance-time And Velocity-time Graphs
Student exploration is a crucial aspect of STEM education, enabling students to actively engage with concepts and develop a deeper understanding. Distance-time and velocity-time graphs play a significant role in this exploration, providing visual representations of motion and helping students analyze and interpret data.
Distance-Time Graphs
Distance-time graphs plot the distance traveled by an object over time. They provide a clear visualization of the object’s motion and allow students to determine the distance covered and the time taken for the movement.
- A linear distance-time graph indicates constant speed.
- A curved distance-time graph indicates varying speed.
- The slope of a distance-time graph represents the object’s velocity.
Velocity-Time Graphs
Velocity-time graphs plot the velocity of an object over time. They provide insights into the object’s speed and direction and allow students to determine the velocity and the time interval for the movement.
- A horizontal velocity-time graph indicates constant velocity.
- A sloping velocity-time graph indicates changing velocity.
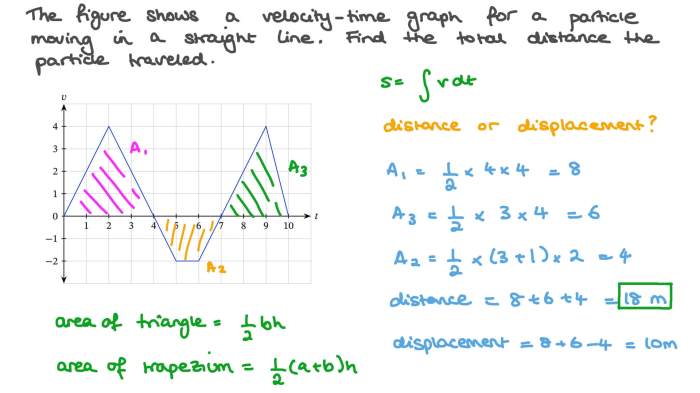
- The area under a velocity-time graph represents the displacement of the object.
Comparing Distance-Time and Velocity-Time Graphs, Student exploration distance-time and velocity-time graphs
Distance-time and velocity-time graphs provide complementary information about motion. Distance-time graphs show the distance covered, while velocity-time graphs show the rate of change of distance.
- The slope of a distance-time graph corresponds to the velocity of the object.
- The area under a velocity-time graph corresponds to the distance traveled.
Applications of Distance-Time and Velocity-Time Graphs
Distance-time and velocity-time graphs have wide applications in various fields, including physics, engineering, and sports.
- In physics, these graphs are used to analyze motion, determine acceleration, and calculate displacement.
- In engineering, they are used to design and optimize systems involving motion, such as vehicles and machinery.
- In sports, these graphs are used to analyze performance, optimize training, and predict outcomes.
Interactive Simulations and Activities
Interactive simulations and activities can enhance student understanding of distance-time and velocity-time graphs.
- Simulations allow students to explore different scenarios and visualize the effects of changing variables on motion.
- Activities, such as analyzing real-world data or designing experiments, help students apply their knowledge and develop problem-solving skills.
Clarifying Questions
What is the significance of student exploration in STEM education?
Student exploration fosters hands-on learning, promotes critical thinking, and cultivates a deep understanding of scientific concepts.
How do distance-time graphs differ from velocity-time graphs?
Distance-time graphs depict the displacement of an object over time, while velocity-time graphs illustrate its velocity over time.
What are some real-world applications of distance-time and velocity-time graphs?
These graphs find applications in fields such as physics, engineering, and sports, aiding in motion analysis, trajectory prediction, and performance optimization.